ALPHAGAN® 0.2%® (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution)
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension:ALP[G]
− as monotherapy in patients in whom topical beta-blocker therapy is contraindicated
− as adjunctive therapy to other intraocular pressure lowering medications when the target IOP is not achieved with a single agent
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% (brimonidine ophthalmic solution)
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% belongs to a class of drugs known as α-2 adrenergic receptor agonistsALP[M]
It is thought that ALPHAGAN® 0.2% may lower IOP by reducing aqueous humour formation and enhancing uveoscleral outflow.ALP[C]
Evidence suggests that ALPHAGAN® 0.2% offers a dual MOAALP[C]
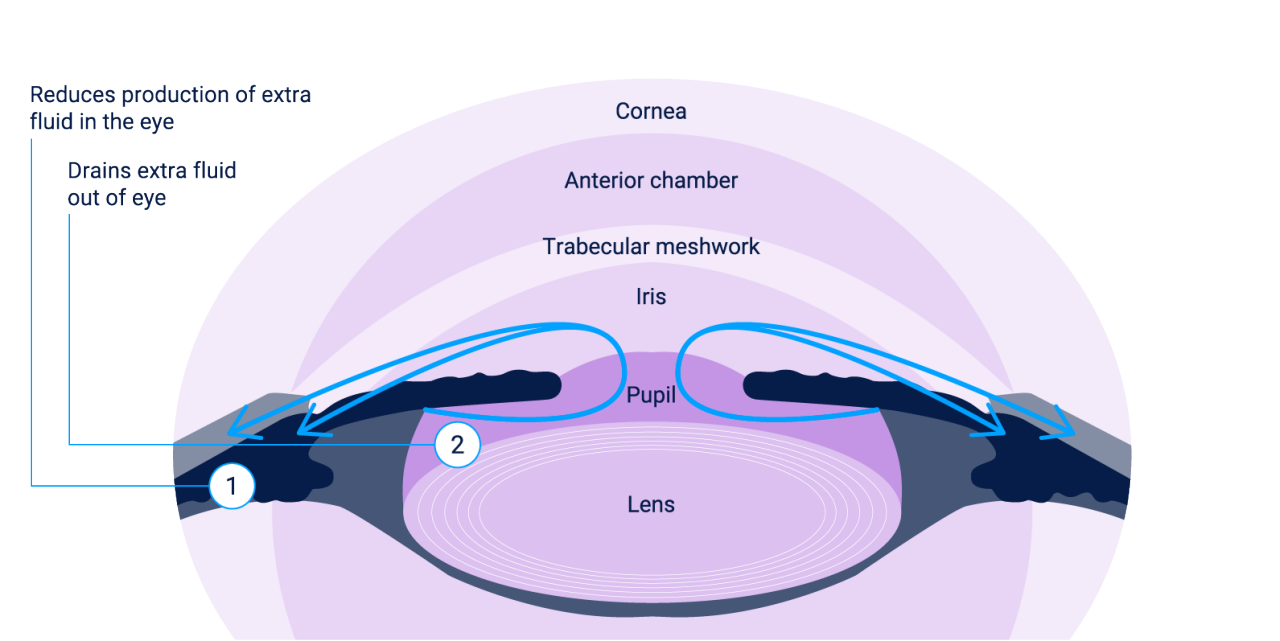
1 – Enhances uveoscleral outflow and reduces aqueous humor production in the ciliary bodyALP1[A], AAO2[A], CLE[A]
Image adapted from American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2017.AAO2[A] Copy from ALPHAGAN® 0.2% Summary of Product Characteristics and Cleveland Clinic. 2022.ALP[C],CLE[A]
Administration and dosing for ALPHAGAN® 0.2%
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% offers twice-daily dosing.ALP[A]
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.ALP[F,G]
- as monotherapy in patients in whom topical beta-blocker therapy is contraindicated
- as adjunctive therapy to other intraocular pressure lowering medications when the target IOP is not achieved with a single agent
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% may not be suitable for some of your patients
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% is contraindicated in:ALP[E,L]
Please refer to ALPHAGAN® 0.2% Summary of Product Characteristics for full safety information and precautions for use.
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.ALP[F,G]
- as monotherapy in patients in whom topical beta-blocker therapy is contraindicated
- as adjunctive therapy to other intraocular pressure lowering medications when the target IOP is not achieved with a single agent
The most commonly reported ADRs are oral dryness, ocular hyperemia and burning/stinging, all occurring in 22 to 25% of patients. They are usually transient and not commonly of a severity requiring discontinuation of treatment. Symptoms of ocular allergic reactions occurred in 12.7% of subjects (causing withdrawal in 11.5% of subjects) in clinical trials with the onset between 3 and 9 months in the majority of patients.ALP[D]
ADR, adverse drug reaction; IOP, intraocular pressure; MOA, mechanism of action.
ALP - ALPHAGAN® (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.2%. Summary of Product Characteristics. 2020.
CLE - Cleveland Clinic. Aqueous Humor & Vitreous Humor. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24611-aqueous-humor-vitreous-humor. Last accessed: April 2024.
AAO2 – American Academy of Ophthalmology. Aqueous Outflow and Glaucoma Drug Mechanisms of Action. Available at: https://www.aao.org/education/basic-skills/animation-of-aqueous-flow. Last accessed: April 2024.

