ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% belongs to a class of drugs known as α-2 adrenergic receptor agonists1
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.1
It is thought that ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% may lower IOP by reducing aqueous humour formation and
enhancing uveoscleral outflow.1
ALPHAGAN® 0.2% (brimonidine ophthalmic solution)
Evidence suggests that ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% offers a dual MOA1
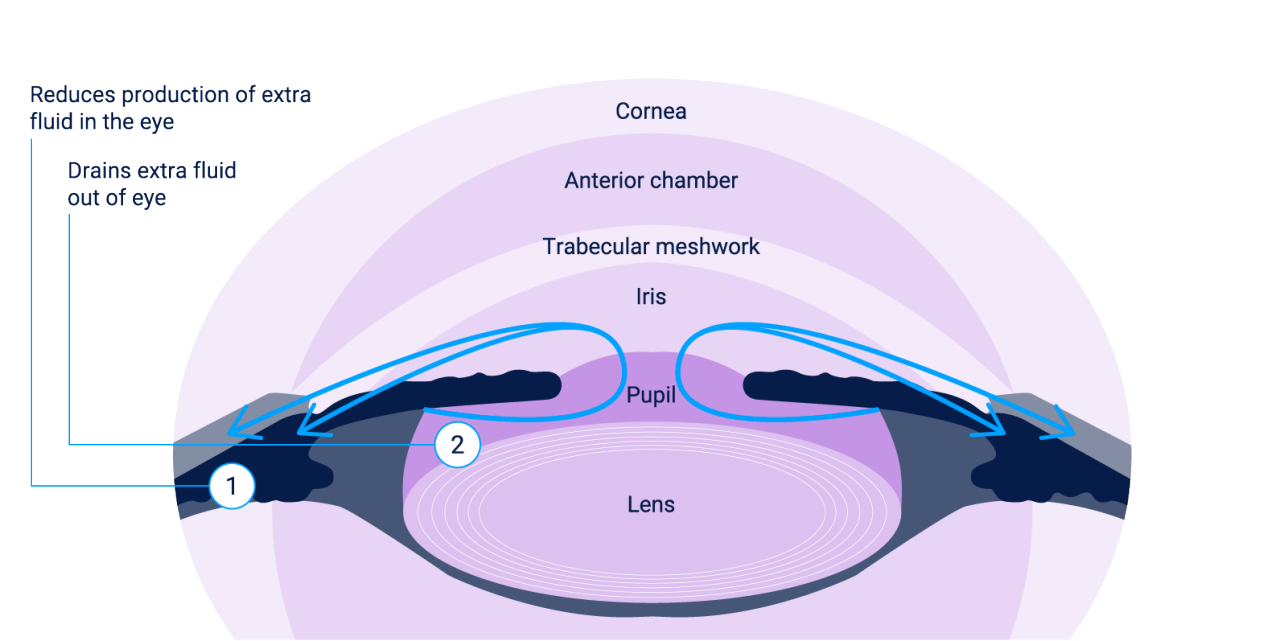
1 – Enhances uveoscleral outflow and reduces aqueous humor production in the ciliary body1–3
Image adapted from American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2017.2 Copy from ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% Summary of Product Characteristics and Cleveland Clinic. 2022.1,3
Administration and dosing for ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15%
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% offers thrice-daily dosing, preserved with Purite®1
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.1
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% may not be suitable for some of your patients
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% is contraindicated in:1
Please refer to ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% Summary of Product Characteristics for
further adverse event and safety information
ALPHAGAN® P 0.1% or 0.15% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.1
Most common adverse reactions occurring in approximately 5% to 20% of patients receiving brimonidine ophthalmic solution (0.1%–0.2%) included allergic conjunctivitis, burning sensation, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, hypertension, ocular allergic reaction, oral dryness, and visual disturbance.1
ADR, adverse drug reaction; BAK, benzalkonium chloride; IOP, intraocular pressure; MOA, mechanism of action.
1. ALPHAGAN® P (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.1% or 0.15%. Prescribing Information. 2013.
2. AAO2 – American Academy of Ophthalmology. Aqueous Outflow and Glaucoma Drug Mechanisms of Action. Available at: https://www.aao.org/education/basic-skills/animation-of-aqueous-flow. Last accessed: May 2024.
3. CLE - Cleveland Clinic. Aqueous Humor & Vitreous Humor. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24611-aqueous-humor-vitreous-humor. Last accessed: May 2024.
4. NOE1. Noecker R. Adv Ther 2001; 18(5) 205–209.

