FIND OUT MORE ABOUT...
SKIN CLEARANCE DATA
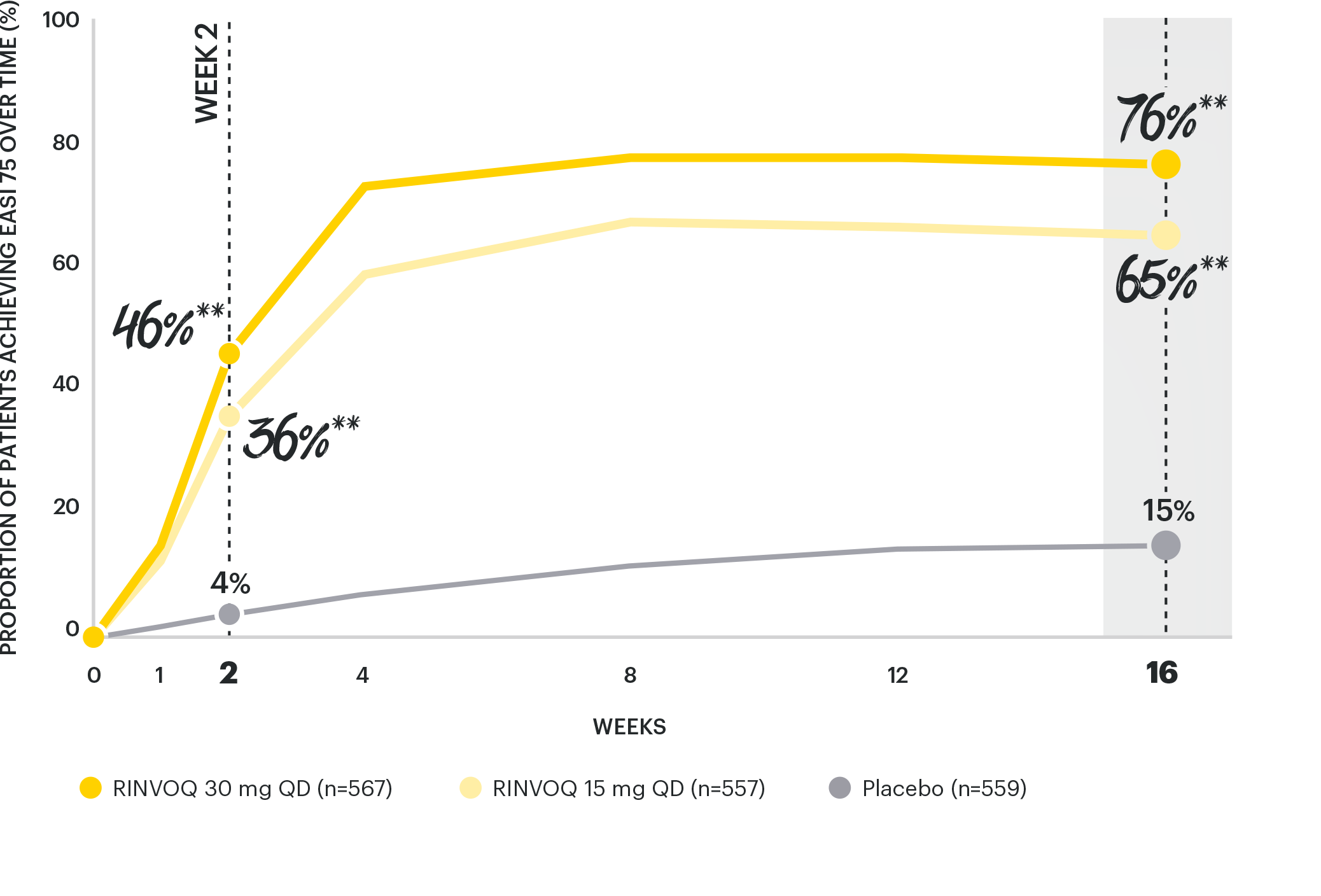
RAPID & ROBUST SKIN CLEARANCE RATES WITH EASI 75
as early as Week 2* and through Week 162,3
*Proportion of subjects achieving EASI 75 by visit in double-blinded period ITT (NRI-C) (placebo-controlled population).2
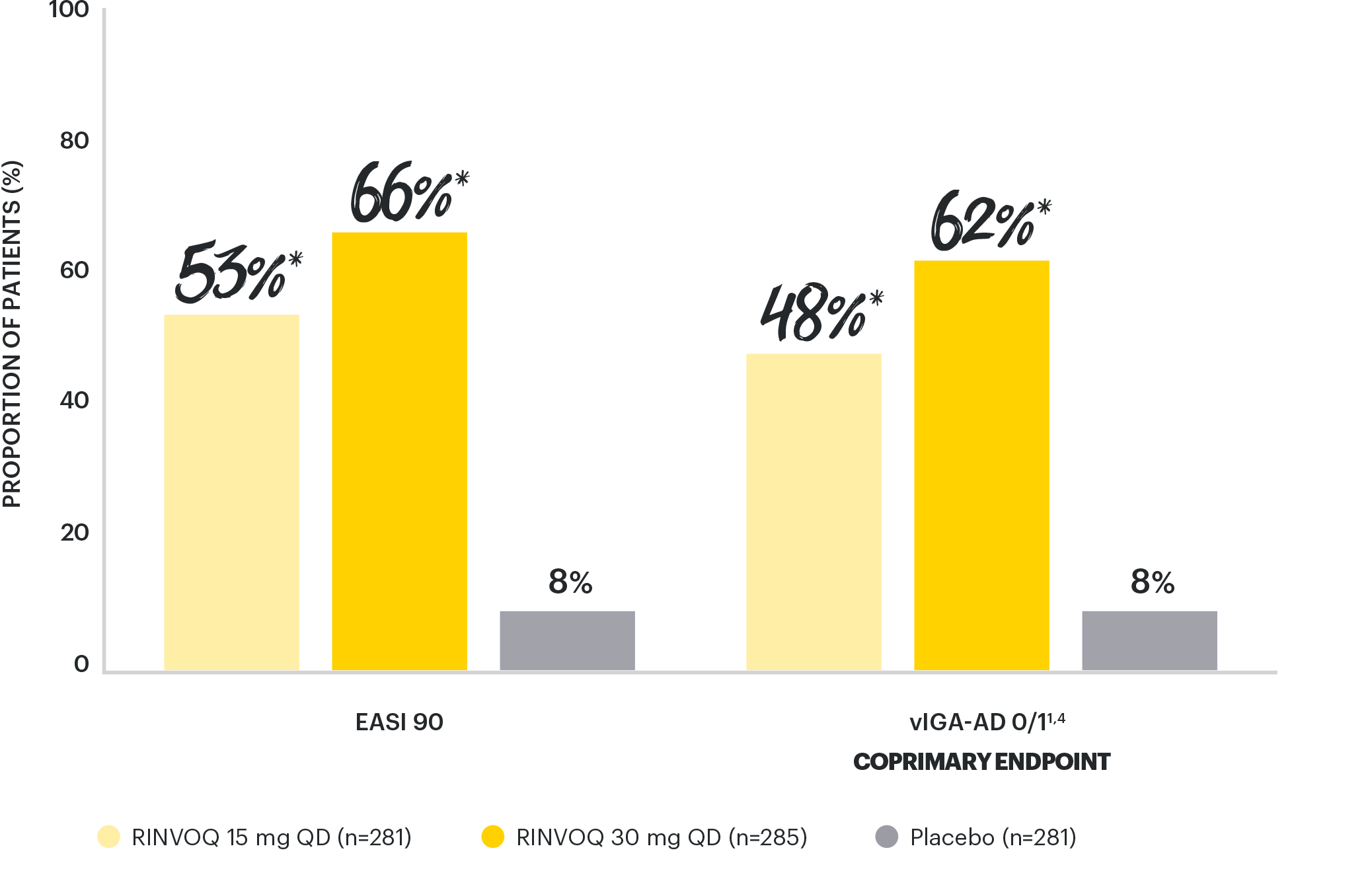
Integrated summary of efficacy of two Phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled studies of 847 (MEASURE UP 1) and 836 (MEASURE UP 2) adult and adolescent (≥12 years of age) with moderate to severe AD. Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to RINVOQ 15 mg (n=281 and 276) or 30 mg (n=285 and 282) QD monotherapy, or placebo (n=281 and 278).1,2
**p<0.001 vs placebo, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C).
AD: atopic dermatitis; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; EASI 75: ≥75% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intention-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; QD: once daily.
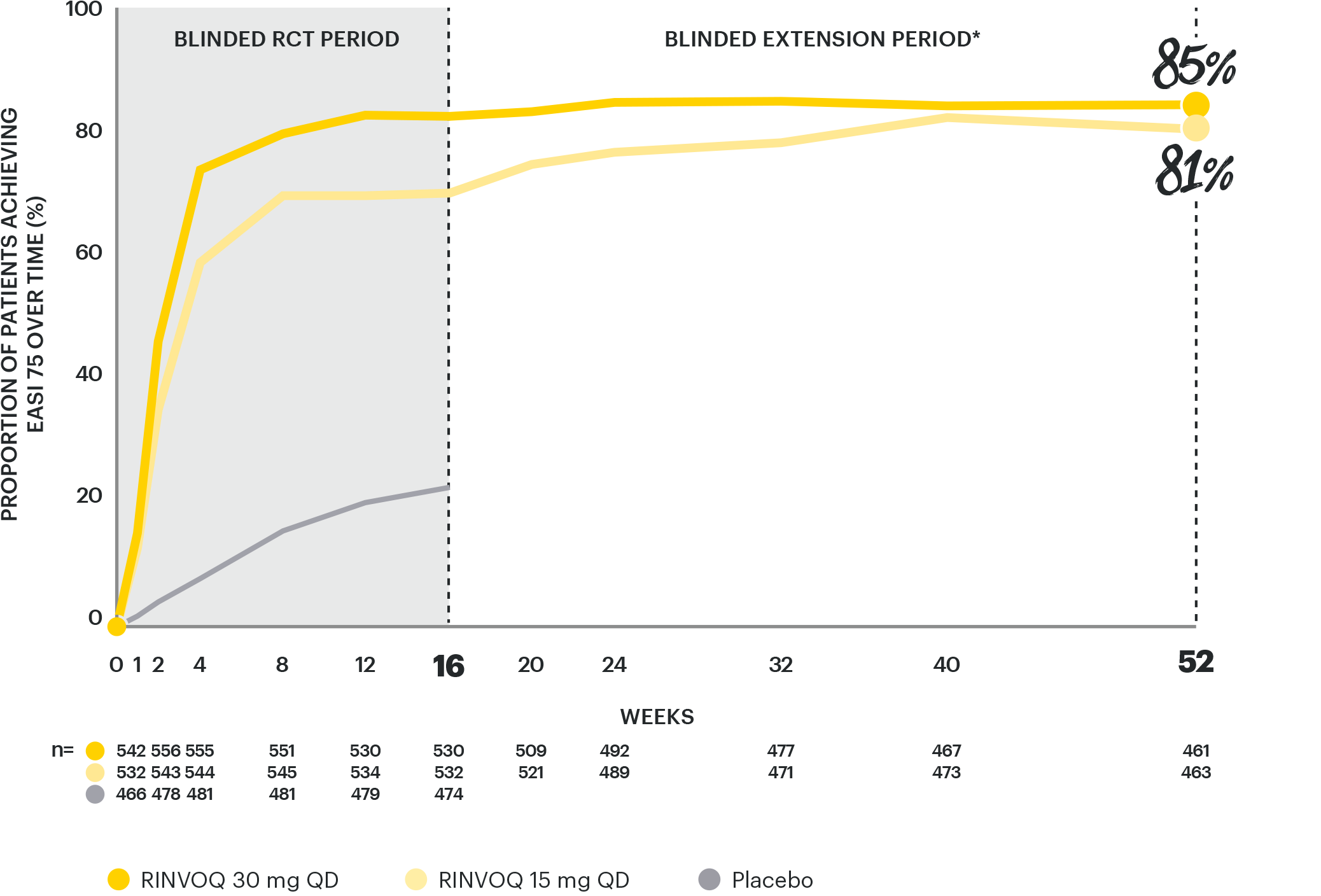
RAPID & LASTING SKIN CLEARANCE RATES WITH EASI 75
through Week 521–4
INTEGRATED ANALYSIS OF MEASURE UP 1 & 22,3
Data are as observed. DATA LIMITATIONS: Data were prespecified non-ranked endpoints not controlled for multiplicity. Observed cases (OC): No imputation of missing data; patients missing data at a visit were excluded from the observed analysis for that visit. There is a potential enrichment as patients who are unable to tolerate or do not respond to drug may drop out. Awareness of active treatment may cause bias related to overall treatment effect. Patients may have used topical medications from Week 16, which were no longer considered rescue.
*TCS were permitted during the blinded extension period and were not counted as rescue therapy.
EASI 75: ≥75% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; QD: once daily; RCT: randomized controlled trial; TCS: topical corticosteroid.
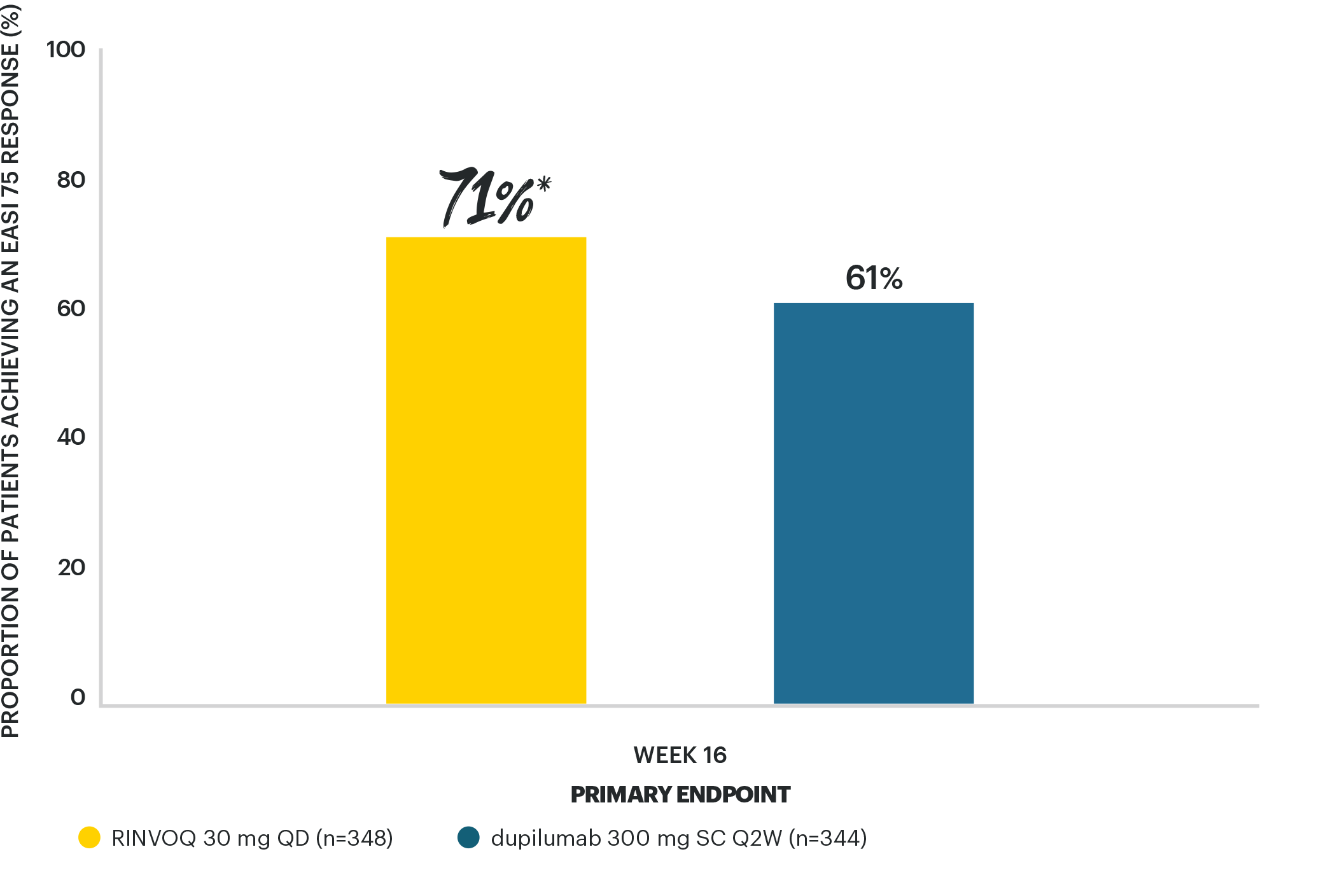
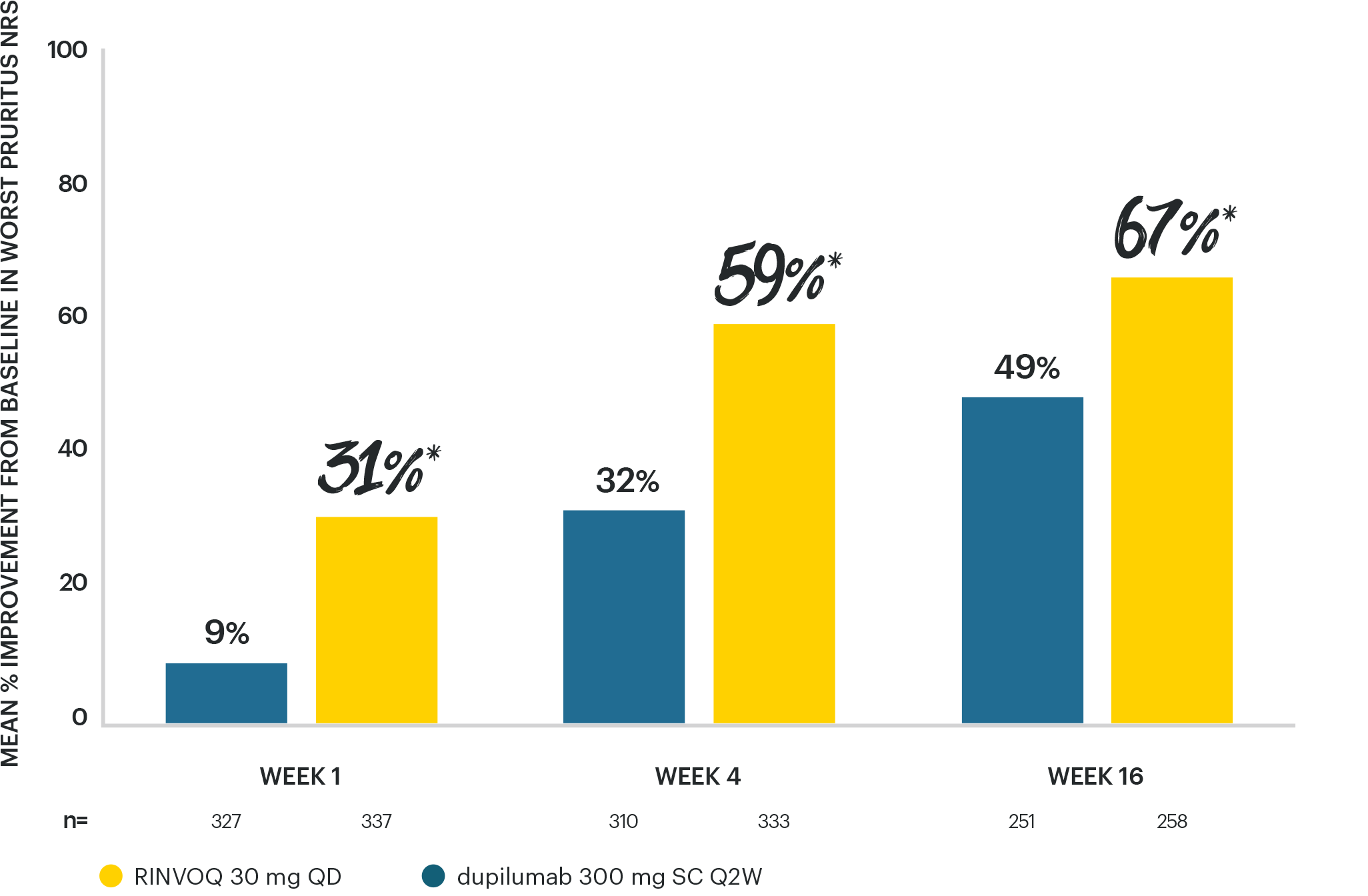
RINVOQ 30 MG ACHIEVED SUPERIORITY VS DUPILUMAB
for EASI 75 at Week 165
*p=0.006 vs dupilumab, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C).
NRI-C, nonresponder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19.
STUDY DESIGN: Phase 3b, randomized, active controlled, double-dummy trial of 692 adult patients with moderate to severe AD. Patients randomized 1:1 to RINVOQ 30 mg QD + placebo SC Q2W for dupilumab (n=348) or dupilumab 300 mg SC Q2W + placebo QD for RINVOQ (n=344). Patients randomized to the dupilumab 300 mg SC Q2W group received the starting dose of 600 mg at the baseline visit.5
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; EASI: Eczema Area and Severity Index; EASI 75: ≥75% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intent-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; QD: once daily; Q2W: every 2 weeks; SC: subcutaneous.
NEARLY COMPLETE SKIN CLEARANCE RATES
vs placebo with both doses at Week 161,4
*p<0.0001 vs placebo, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C); all timepoints.
EASI 90 at Week 16 was a ranked secondary endpoint.
AD: atopic dermatitis; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; EASI 90: ≥90% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intent-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; QD: once daily; vIGA-AD: validated Investigator’s Global Assessment for AD.
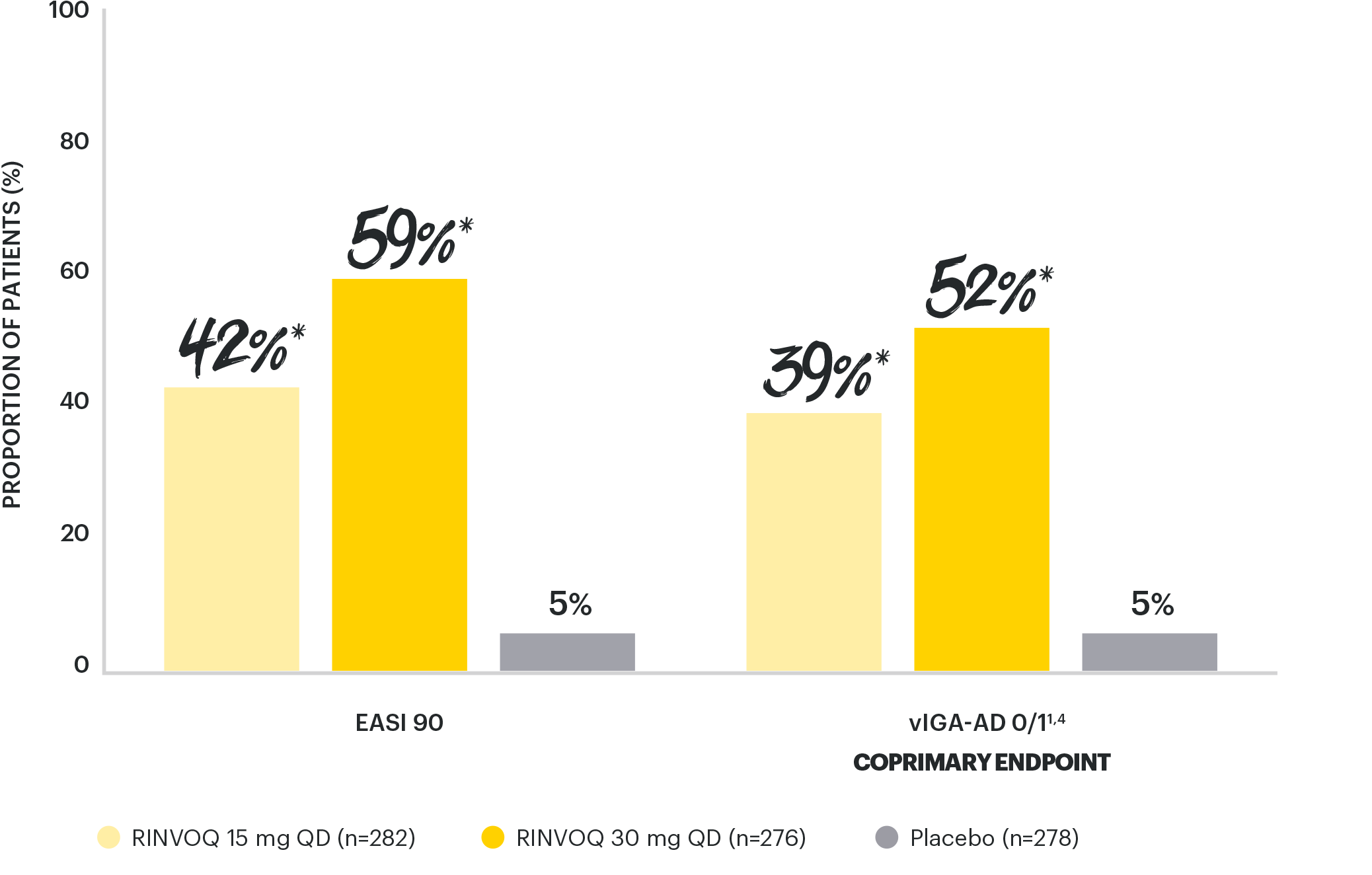
NEARLY COMPLETE SKIN CLEARANCE
rates vs placebo with both doses at Week 161,4
*p<0.0001 vs placebo, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C).
EASI 90 at Week 16 was a ranked secondary endpoint.
AD: atopic dermatitis; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; EASI 90: ≥90% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intent-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; QD: once daily; vIGA-AD: validated Investigator’s Global Assessment for AD.
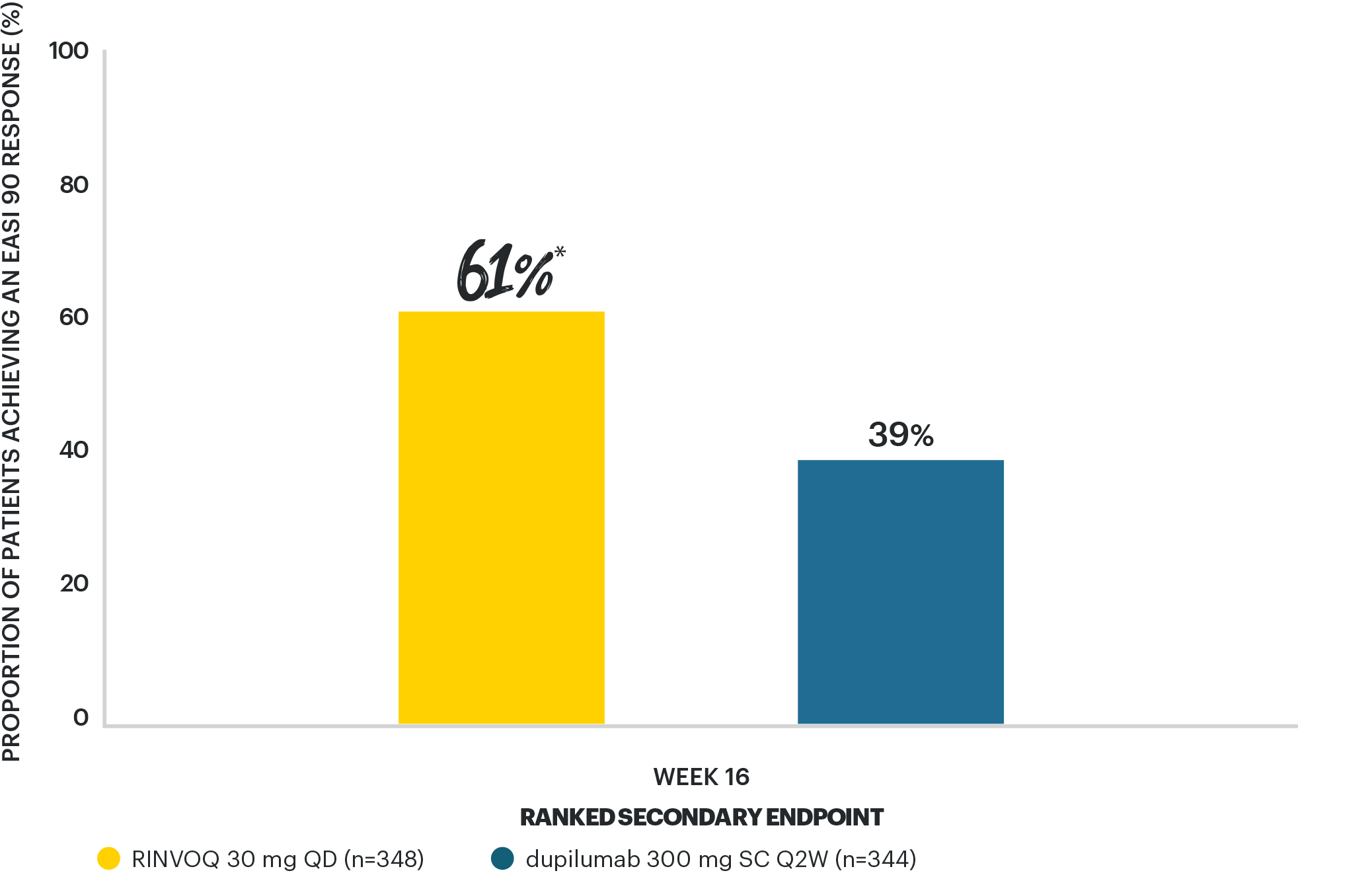
RINVOQ 30 MG ACHIEVED SUPERIORITY VS DUPILUMAB FOR EASI 90
at Week 165
*p<0.001 vs dupilumab, multiplicity-controlled ITT (NRI-C).
NRI-C, nonresponder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19.
EASI 90/100 are stringent assessment criteria, where EASI 100 is complete skin clearance (EASI score of 0).
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; EASI: Eczema Area and Severity Index; EASI 90/100: ≥90/100% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intent-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; QD: once daily; Q2W: every 2 weeks; SC: subcutaneous.
ITCH REDUCTION DATA
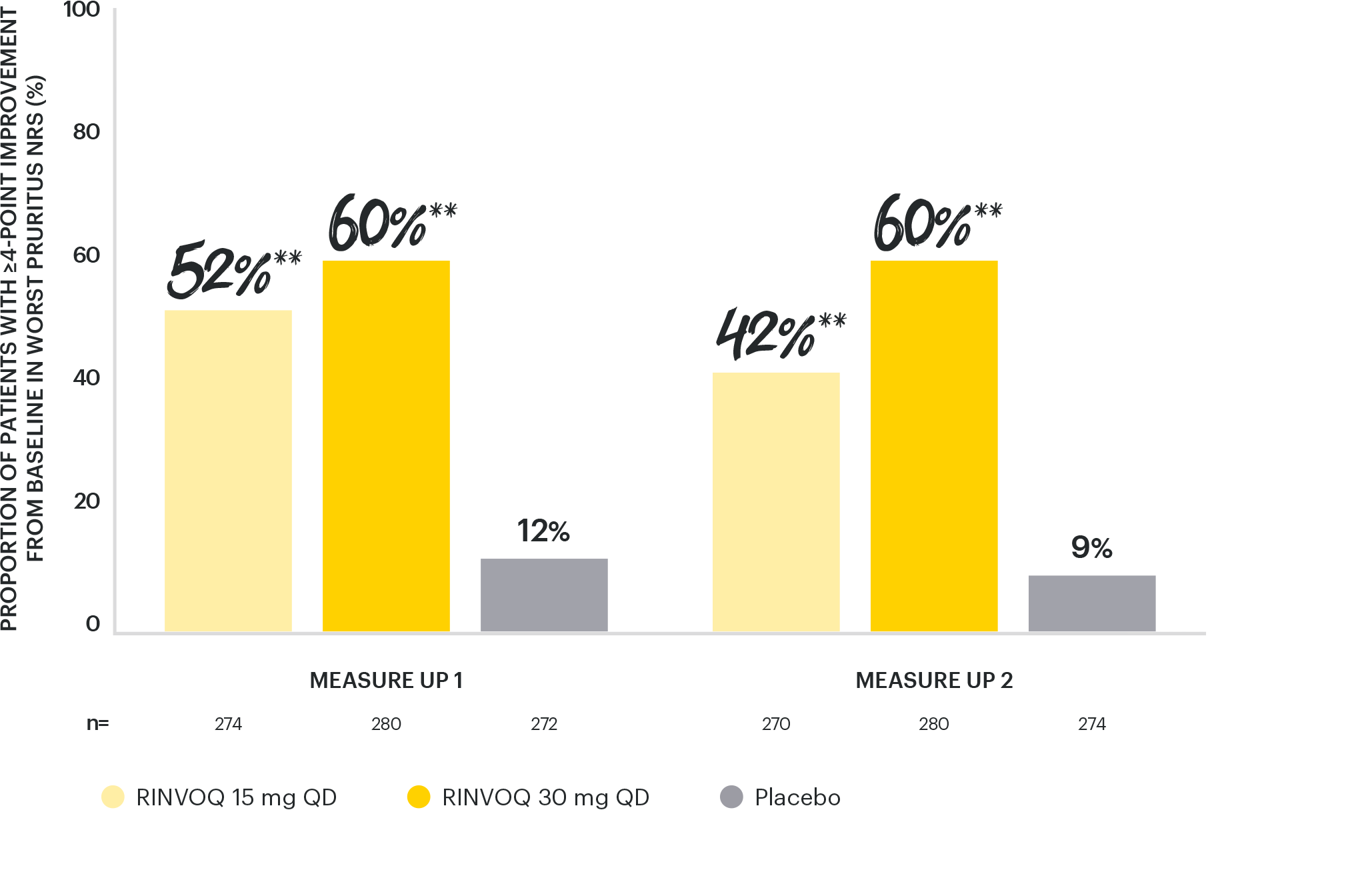
RAPID & SIGNIFICANT ITCH REDUCTION
vs placebo with both doses at Week 161,4
ITCH REDUCTION (IMPROVEMENT IN WORST PRURITUS NRS ≥4)
*p=0.0003 vs placebo, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C).
**p<0.0001 vs placebo, multiplicity-controlled analysis ITT (NRI-C).
Itch reduction (≥4 point improvement in Worst Pruritus NRS from baseline assessed in patients with Worst Pruritus NRS ≥4 at baseline) at Day 1 & 2 after treatment initiation for RINVOQ 30 mg and 15 mg, respectively, and at Week 16 for both doses were ranked secondary endpoints.1,4
ITT: intention-to-treat; MI: multiple imputation; NRI-C: non-responder imputation incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19; NRS: numerical rating scale; QD: once daily.
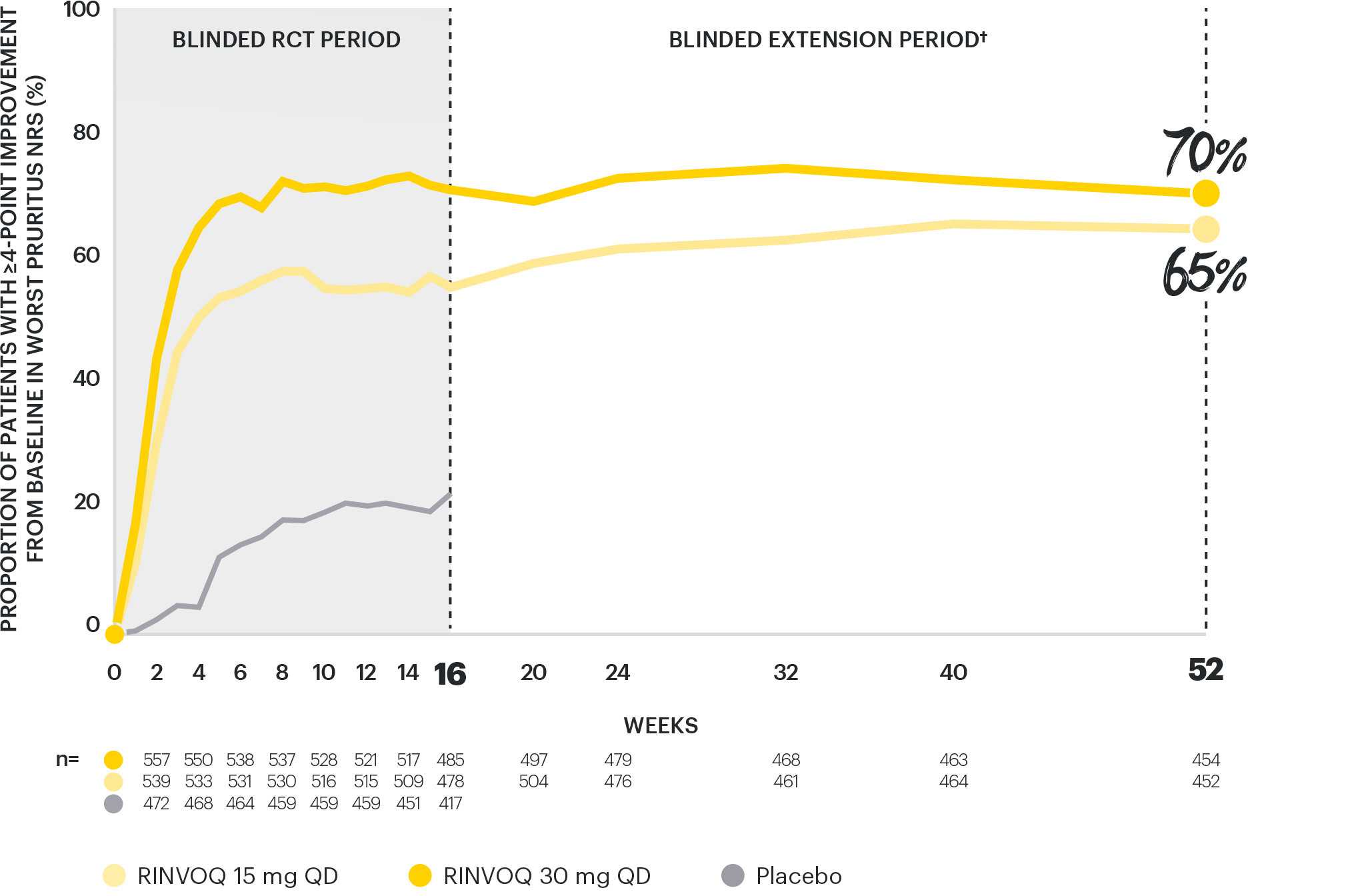
RAPID & LASTING ITCH REDUCTION
with both doses, through Week 521–4
INTEGRATED ANALYSIS OF MEASURE UP 1 & 2:
ITCH REDUCTION (IMPROVEMENT IN WORST PRURITUS NRS ≥4)2,3
Data are as observed. DATA LIMITATIONS: Data were prespecified non-ranked endpoints not controlled for multiplicity. Observed cases (OC): No imputation of missing data; patients missing data at a visit were excluded from the observed analysis for that visit. There is a potential enrichment as patients who are unable to tolerate or do not respond to drug may drop out. Awareness of active treatment may cause bias related to overall treatment effect. Patients may have used topical medications from Week 16, which were no longer considered rescue.
†TCS use was permitted during the blinded extension period (Week 16 to Week 52) and was not counted as rescue therapy.
NRS: numerical rating scale; QD: once daily; RCT: randomized controlled trial; TCS: topical corticosteroid.
RINVOQ 30 MG ACHIEVED SUPERIORITY VS DUPILUMAB
for improvement in itch as early as Week 1 and at Week 165
*p<0.001 vs dupilumab ITT (MMRM).
STUDY DESIGN: Phase 3b, randomized, active-controlled, double-dummy trial of 692 adult patients with moderate to severe AD. Patients were randomized 1:1 to RINVOQ 30 mg QD + placebo SC Q2W for dupilumab (n=348) or dupilumab 300 mg SC Q2W + placebo QD for RINVOQ (n=344). Primary endpoint was EASI 75 at Week 16. Itch reduction (percent improvement in Worst Pruritus NRS from baseline) vs dupilumab at Weeks 1, 4, and 16 were ranked secondary endpoints.5
EASI 75: ≥75% reduction in Eczema Area and Severity Index; ITT: intent-to-treat; MMRM: mixed model for repeated measures; NRS: numerical rating scale; QD: once daily; Q2W: every 2 weeks; SC: subcutaneous.
REFERENCES
- RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) Summary of Product Characteristics. AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG: June 2022.
- Simpson E, Papp K, Blauvelt A, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis: Results Through Week 52 From Replicate, Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies: Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2. Poster at the 2021 Dermatology Education Foundation (DEF) Essential Resource Meeting (DERM2021), August 5–8, 2021, Las Vegas NV, USA.
- Simpson EL, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: analysis of follow-up data from the Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158(4):404–413.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira H, Simpson E, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021; 397(10290): 2151–2168.
- Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib vs Dupilumab in Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(9):1047–1055.